In this tutorial you will learn how to compose Languages.
To ilustrate this we will take MiniFSM Language as base and add it an Action Language executed when states are activated and an Expression Language improve the expressivness of Transitions.
To setup your workspace, import the followings projects in your workspace:
(checkout the git repository https://github.com/diverse-project/melange-examples and import the following projects)
– MiniFSM metamodel: MiniFSM/languageProjects/fr.inria.diverse.minifsm
– MiniFSM interpreter: MiniFSM/languageProjects/fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.interpreter
– MiniLang metamodel: MiniFSM/languageProjects/fr.inria.diverse.minilang
– MiniLang interpreter: MiniFSM/languageProjects/fr.inria.diverse.minilang.interpreter
MiniFSM is the Language build in the tutorial [Define an executable DSL].
MiniLang is a Language describing operations of Integer, with Variables and Expressions.
We will define Melange languages based on theses imported projects.
Create a new Melange project:
- Open the menu
File > New > Project...and selectMelange > Melange Project, then clickNext.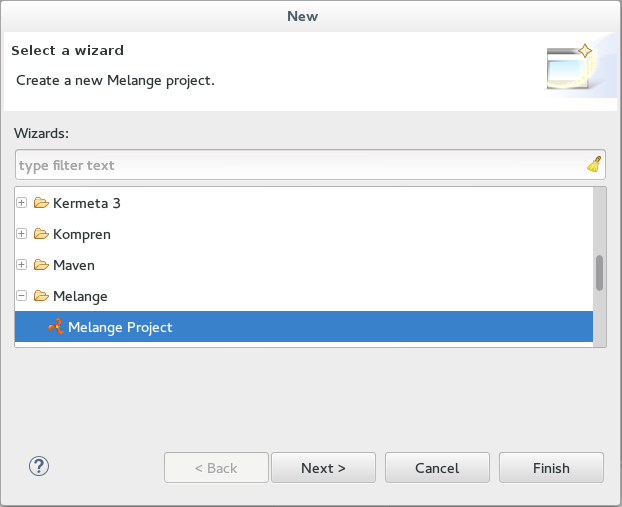
- Name the project “fr.inria.diverse.melange.fsm” and click
Next.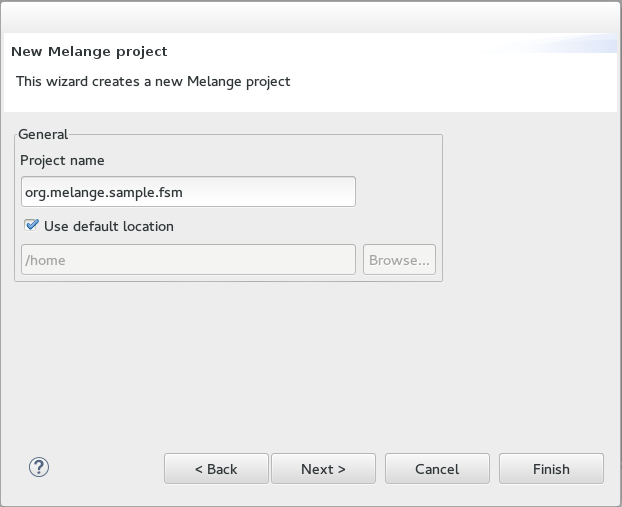
- Check
Create a plug-in using one of the templatesand selectSimple Melange project, thenNext.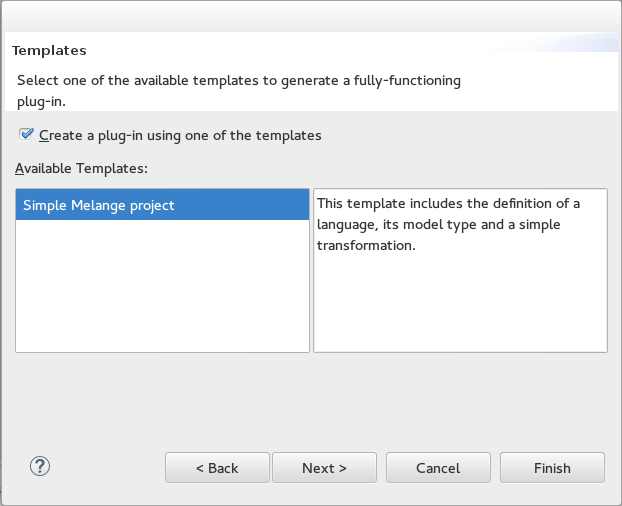
- Fill the fields:
- Package -> fr.inria.diverse.melanger
- Melange file name -> Main
- Language name -> MiniFSM
- Browse the Ecore file location to select minifsm.ecore from the “fr.inria.diverse.minifsm” project
Then click the
Finishbutton.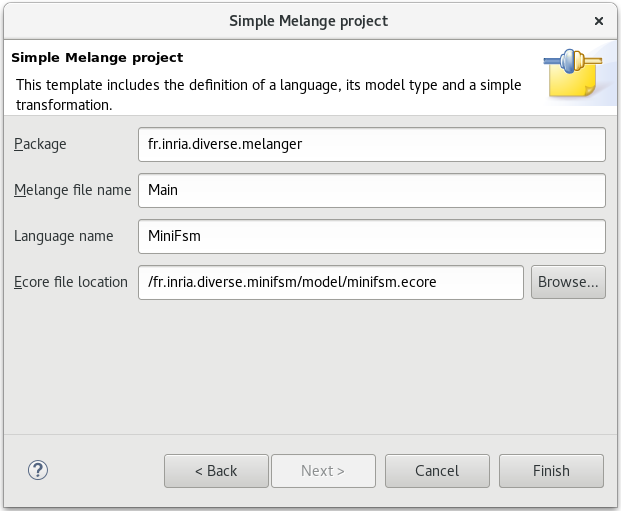
- Open the
META-INF/MANIFEST.MFand in thedependenciestab add Plug-ins- fr.inria.diverse.minilang
- fr.inria.diverse.minilang.interpreter
- fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.interpreter
- fr.inria.diverse.minifsm should be already there thanks to the wizard.
This step is needed to have both metamodel and interpreter projects in the classpath of the Melange project.
Your Main.melange should look like this:
package fr.inria.diverse.melanger
language MiniFsm {
syntax "platform:/resource//fr.inria.diverse.minifsm/model/minifsm.ecore"
exactType MiniFsmMT
}
transformation foo(MiniFsmMT model) {
val root = model.contents.head
print("root: " + root)
}
@Main
transformation main() {
val m1 = MiniFsm.load("input/Simple.xmi")
foo.call(m1)
}
Delete the generated transformations, we will not use it.
Add the aspects defined in the “fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.interpreter” project.
with minifsm.aspects.FinalStateAspect
with minifsm.aspects.TransitionAspect
with minifsm.aspects.StateAspect
with minifsm.aspects.FSMAspect
You can use the content assist here by selecting --Import existing DSA project--
It will scan the selected project to find Aspects and declare them in the current Language.
Create another Language “MiniActionLang” based on:
- minilang.ecore (the metamodel of a program)
- Context.ecore (represent the execution state)
The content assist is also available after the keyword syntax by pressing Ctrl+Space.
It gives direct access to .ecore files in the workspace.
And finally add the Aspects from the fr.inria.diverse.minilang.interpreter project.
The Main.melange file now contains:
package fr.inria.diverse.melanger
language MiniFsm{
syntax "platform:/resource/fr.inria.diverse.minifsm/model/minifsm.ecore"
with minifsm.aspects.FinalStateAspect
with minifsm.aspects.TransitionAspect
with minifsm.aspects.StateAspect
with minifsm.aspects.FSMAspect
}
language MiniActionLang{
syntax "platform:/resource/fr.inria.diverse.minilang/model/minilang.ecore"
syntax "platform:/resource/fr.inria.diverse.minilang.interpreter/model/Context.ecore"
with minilang.aspects.IntegerAspect
with minilang.aspects.IntVariableRefAspect
with minilang.aspects.LessAspect
with minilang.aspects.IntExpressionAspect
with minilang.aspects.VariableRefAspect
with minilang.aspects.IntAssignmentAspect
with minilang.aspects.BooleanExpressionAspect
with minilang.aspects.BooleanVariableRefAspect
with minilang.aspects.BlockAspect
with minilang.aspects.PlusAspect
with minilang.aspects.BooleanAssignmentAspect
with minilang.aspects.IntOperationAspect
with minilang.aspects.EqualAspect
with minilang.aspects.IntComparisonAspect
with minilang.aspects.GreaterAspect
with minilang.aspects.BooleanAspect
with minilang.aspects.StatementAspect
with minilang.aspects.MinusAspect
with minilang.aspects.NotAspect
with minilang.aspects.DivideAspect
with minilang.aspects.MultiplyAspect
with minilang.aspects.LessOrEqualAspect
with minilang.aspects.GreaterOrEqualAspect
with minilang.aspects.AndAspect
with minilang.aspects.OrAspect
with minilang.aspects.BooleanOperationAspect
with minilang.aspects.PrintVarAspect
with minilang.aspects.PrintStrAspect
}
Now we create the MelangedLang that will merge the previous Languages.
We will inherits MiniFsm since we want all its syntax and behavior.
language MelangedLang inherits MiniFsm {
}
We need to merge MiniActionLang but we dont want the If and While EClasses because the control flow is already expressed in MiniFSM.
So we use the slice operator to keep only the selected EClasses.
Since MiniFsm and MiniActionLang have different name for their root EPackage we have to rename them, otherwise will we have two roots. It is done by the renaming keyword.
language MelangedLang inherits MiniFsm {
slice MiniActionLang on [
'Plus','Minus','Multiply','Divide','Less','LessOrEqual',
'Greater','GreaterOrEqual','Equal','Not','Or','And','IntVariableRef',
'BooleanVariableRef', 'Integer', 'Boolean',
'BooleanAssignment', 'IntAssignment', 'Block', 'PrintVar', 'PrintStr',
'Context','BooleanVar','IntegerVar'] renaming {
'minilang' to 'minifsm'
}
}
Now we have merged the two metamodels we still need to link their concepts.
Indeed Transition should have Expression, State needs Instructions and FSM will have an execution context.
We could add theses missing EReferences by merging another .ecore file but as we need to do some adjustments in the semantics.
We will create new K3 Aspects to take in account the merged syntax.
Do a right click on the package fr.inria.diverse.melanger in the Melange project and create an new file Glue.xtend.
Create a new Aspect “FsmGlue” on FSM extending FSMAspect.
Add a new attribute Context annotated with @Containment to instantiate it when an FSM is created.
It have to be public to be added in the abstract syntax by Melange.
package fr.inria.diverse.melanger
import fr.inria.diverse.k3.al.annotationprocessor.Aspect
import fr.inria.diverse.k3.al.annotationprocessor.Containment
import fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.FSM
import fr.inria.diverse.context.minilang.Context
import minifsm.aspects.FSMAspect
@Aspect(className=FSM)
class FsmGlue extends FSMAspect {
@Containment
public Context context
}
Add a contained Block in State.
We override StateAspect.execute() to take in account the new Block.
@Aspect(className=State)
class StateGlue extends StateAspect {
@Containment
public Block block
override void execute(){
_self.block?.execute(_self.fsm.context)
}
}
Add BooleanExpression inside Transition.
Override TransitionAspect.isActivated() to evaluate the new Expression.
@Aspect(className=Transition)
class TransitionGlue extends TransitionAspect {
@Containment
public BooleanExpression expression
override boolean isActivated(){
return _self.expression === null || _self.expression.eval(_self.fsm.context)
}
}
The Glue.xtend file should contains at the end:
package fr.inria.diverse.melanger
import fr.inria.diverse.k3.al.annotationprocessor.Aspect
import fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.FSM
import fr.inria.diverse.context.minilang.Context
import fr.inria.diverse.k3.al.annotationprocessor.Containment
import fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.State
import fr.inria.diverse.minilang.Block
import fr.inria.diverse.minifsm.Transition
import fr.inria.diverse.minilang.BooleanExpression
import minifsm.aspects.FSMAspect
import minifsm.aspects.StateAspect
import static extension fr.inria.diverse.melanger.FsmGlue.*
import static extension minilang.aspects.BlockAspect.*
import static extension minilang.aspects.BooleanExpressionAspect.*
import minifsm.aspects.TransitionAspect
@Aspect(className=FSM)
class FsmGlue extends FSMAspect {
@Containment
public Context context
}
@Aspect(className=State)
class StateGlue extends StateAspect {
@Containment
public Block block
override void execute(){
_self.block?.execute(_self.fsm.context)
}
}
@Aspect(className=Transition)
class TransitionGlue extends TransitionAspect {
@Containment
public BooleanExpression expression
override boolean isActivated(){
return _self.expression === null || _self.expression.eval(_self.fsm.context)
}
}